Contributed by Vineet Patel
To surveyors, BIM has thrown open endless possibilities. From the days of 2D topographic surveys, floor plans, and elevations, surveyors have moved forward to laser scanning, UAV photogrammetry, point clouds, LIDAR, 3D models, and intelligent models.
A further crucial shift, however, is happening in the role of surveyors in the BIM environment. And that shift, a logical consequence of integrating BIM and geographic information system (GIS) in construction management, is that surveyors are assuming a central role in the backdrop of Industry 4.0.
A step forward: The role shift of surveyors in Industry 4.0
While admitting that BIM means different things to surveyors according to their roles and organizational objectives, a July 2020 report, ‘The future of BIM: Digital transformation in the UK construction and infrastructure sector,’ by the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors, UK, (RCIS) lays out the shift. The report observes that the utility of BIM to surveyors has now progressed to ‘owning information management’ and to connecting with other Industry 4.0 technologies.
From the isolated phases of 2D drawings and manual and single-discipline 3D model approach, where information is limited, BIM is seen to be evolving through 3D collaboration models.
Changes in BIM standards redefining a surveyor’s focus and task load
To help BIM reach its true potential, surveyors will need to standardize their information flow and put in controls over everything inconsequential to their core services.
It is now information management, and not technology, that defines the maturity level of BIM. Technology’s role is to provide methods to create efficiencies, information management creates the worldview, strategy creation, and implementation. Therefore, surveyors need to get on top of information management through BIM.
We believe that Surveyors can leverage BIM opportunities throughout every project life-cycle – from pre-construction to operations and become major contributors to the BIM revolution.
How can surveyors play the role of progressive BIM enablers?
Surveyors need to engage with other disciplines and contractors to create value-driven deliverables. Based on a single project management tool and BIM-ready deliverables, surveyors can collaborate with various disciplines to gain a thorough understanding of design and spatial geometry or data to ensure efficient construction.
Consequently, they can create “intelligent information-based” models for clients to consume data downstream. This is because surveying professionals and firms understand the existing BIM framework within which they work, and leverage technology to deliver end-users with vital information for better asset management.
As survey tools become more advanced, it isn’t mere static data, but location-based information that will continue to unfold over time.
The pivotal role of Surveying in BIM
Surveyors are geospatial experts who provide BIM-based information. Modern surveyors need to provide data-intensive deliverables that include site contours, surface models and conditions, orientation, site configurations, etc.
They need to measure data using various techniques and formats if they are to deliver expertise and service offerings. BIM isn’t just used for building modeling, but it is also applied to infrastructure for improved visualization and clash detection.
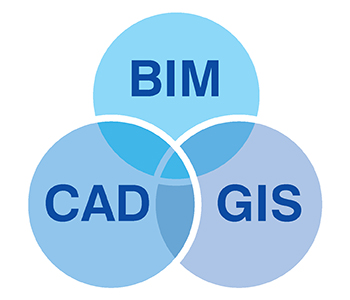
While the BIM model is an undisputed source of data, it needs to be interoperable with other systems like GIS and CAD for better data structure and organization.
Making design and pre-construction more valuable with key contributions by surveyors
During the project planning stage, surveyors play a pivotal role in capturing As-Built site conditions through scanning and tools. They can provide greater value with 3D visualization to enhance spatial awareness of As-Built assets and detailed documentation.
With precise mesh geometry, terrain models, locations, etc. the transition from design to fabrication, construction, and installation can be seamless, leading to lower rework and reduced RFI’s.
Setting up an on-site control network to identify construction elements and greater quality control
Deploying BIM models in the field is an ideal solution to extract detailed prefabrication drawings to improve onsite installation. Additional insights through AR/VR, AI, and mixed reality technology can help enhance field connectivity and performance. With up-to-date surveyed documentation, onsite teams can plug installation gaps to improve constructability.
Defining problems better with precise simulations and calculations
Developing maintenance and management plans using simulations based on 3D models can expedite operations while saving costs. Accurate As-Built information and metadata can assist surveyors to identify crucial building objects required on the job site. As-Built scans and imaging help facilities managers, owners, and occupants to manage buildings and infrastructure more efficiently.
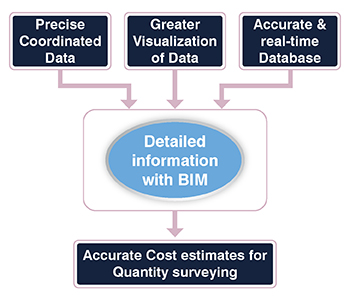
3 BIM capabilities for Quantity Surveyors that are valuable assets for Quantity Surveying practice
Information Visualization, Database Reliability, and Data Coordination are 3 crucial BIM pillars surveyors can implement to enhance design intent, produce reliable cost estimates, build accurate BOQ’s, draw accurate QTO’s, etc.
1. Better information delivery with information-rich 3D visualization.
Effective project management requires project visualization to drive information transmission. Furthermore, visualization enables 3D model views to augment constructability and design intent based on simulations and interactions.
BIM capabilities mapped to 3D data visualization include –
- Costing analysis (5D)
- BOQ preparation with 3D models
- Project conceptualization and planning
- Simulation and value engineering
- Tendering and estimating
- Drawing interpretation and data extraction
2. Enhanced database reliability to symbolize project elements and objects.
A BIM model draws information about costs, dimensions, materials, and other parameters related to building elements. Rather than producing a set of siloed 2D drawings, a rich dataset provides reliable information about functional and physical characteristics through intelligent objects.
A robust database promotes accurate quantity extraction of building objects and materials leading to on-point cost estimates.
BIM capabilities mapped to data reliability include –
- Interoperable IFC views for preparation of BOQ’s
- Quantity Takeoff’s and cost estimates
- Post-construction cost management
- Identification of design changes or prototypes
3. Drive improved data coordination between offsite and onsite teams.
Coordinated BIM models can communicate vital data between people on the construction field and back-office. Combining data into a single model improves communication between design, engineering, and construction trades. Furthermore, surveyors can access vital data to analyze estimates based on virtual models, consequently reducing errors and rework.
BIM capabilities mapped to data coordination include –
- Estimation based on virtual 3D models
- Project-wide access to information and better communication
A world of technology awaits surveying professionals
Emerging technology like mixed-reality has helped construction teams simplify complex design and construction issues. With rapidly changing project requirements, Mixed Reality could drive holographic technology to display a 1:1 scale model and experience physical space through a wearable lens. Optimizing large-scale building models through gamification tools will continue to be a valuable asset for surveyors and other stakeholders.
BIM has proved to be a clear winner as it delivers projects within time and budget. With expertise in spatial data, surveyors are well-positioned to become reliable partners for BIM-based projects. They can also set long-term relationships with multiple stakeholders across the entire project to build a profitable business.
Conclusion
With geospatial knowledge and updates of accurate and dependable data, surveyors ensure maximum precision in project execution, from the phase of bare site topography development to structural erection.
Surveyors today are moving to a more central role in the BIM environment, because the accuracy and validity of asset information in a construction project, and its real-time dissemination, have become viable and streamlined.
 Vineet Patel is a BIM manager and a “Performance excellence” awardee working at Hitech CADD services. Having worked on multiple MEP and Scan to BIM projects globally, Vineet has successfully enhanced design quality and project productivity through the latest BIM tools and technology interventions. From smart Revit content creation for products to clash-free MEP layouts, his exposure to various residential and commercial sectors makes him a go-to authority for MEP BIM.
Vineet Patel is a BIM manager and a “Performance excellence” awardee working at Hitech CADD services. Having worked on multiple MEP and Scan to BIM projects globally, Vineet has successfully enhanced design quality and project productivity through the latest BIM tools and technology interventions. From smart Revit content creation for products to clash-free MEP layouts, his exposure to various residential and commercial sectors makes him a go-to authority for MEP BIM.






