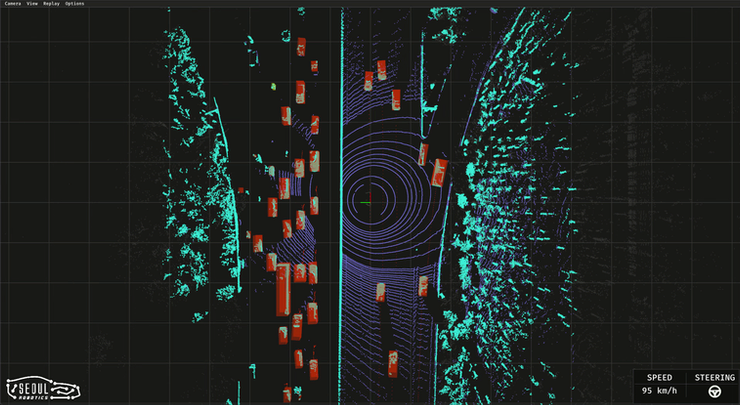
Seoul Robotics is a 3D computer vision company that uses AI and machine learning in intelligent robotic perception systems. In July, they launched Voyage, a plug-and-play lidar system that comes pre-equipped with the company’s perception software.
While the market for lidar sensors has recently boomed due to the pursuit of autonomous vehicles, most lidar sensors are sold without onboard intelligence or pre-loaded software. Seoul Robotics aims to lower the barrier to entry for those wanting to use 3D perception by helping to make them “smart” and immediately usable.
Founded in 2017, Seoul Robotics released their first device of this type, called Discovery, in the beginning of 2021 which they heralded as a “plug-and-play lidar perception system.” Discovery utilizes their SENSR (Sensor-Agnostic Perception Software to democratize Lidar) software which was released at the same time and showcased at the virtual edition of CES in 2021.
Users of Discovery can operate up to 10 individual lidar sensors off one LPU (Lidar Processing Unit) depending on which tier (Discovery One, Discovery Plus, or Discovery-X) is purchased. Each model contains a unique LPU. The main difference between each LPU model (LPU-1, LPU-8, or LPU-L) is the number of lidar sensors each processing to which each unit can connect. These sensors do not need to be from Seoul Robotics either due to their patented software, making the technology essentially sensor-agnostic.
Utilizing the same onboard software as Discovery, Voyage is a low-power version with optional wi-fi access that seems ideal for smaller or less invasive uses. An additional solution, Endeavor, provides the opposite with the ability to connect with up to eight Lidar sensors. This “Deployment Ready Kit” is said to, “solve(s) larger-scale problems,” which expands the scope of usage for businesses that need more in-depth Lidar coverage.
The software in each LPU is SENSR 2.0. SENSR is an open-source computer vision software that uses deep learning to create 3D models of the world in real time. Seoul Robotic states that SENSR is the, “first open-platform, sensor independent 3D tracking solution available in the market.” The universality of the software allows for hardware flexibility (with more than 70 brands currently supported), which is a major selling point and helps to realize their goals of democratizing lidar. It seems that Seoul Robotics is essentially trying to become the Android operating system, as opposed to iOS, of the lidar world.
This sensor-agnostic, open-source accessibility along with the “plug and play” aspect could potentially revolutionize the scope of lidar usage. As more companies produce lidar with onboard software, the applications of lidar could grow exponentially. What are some possibilities of allowing this technology into the hands of more businesses?
Obviously, this low-cost innovation allows the automotive industry to begin an uptick in the production of self-driving or AI-operated vehicles, since the cost of lidar for such a new fleet of vehicles was cost preventive in the past. The ease of deployment and consistent software may be attractive to automotive manufacturers. Their software is currently deployed by top-tier organizations such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Chattanooga Department of Transportation, Emart, among others.
A less obvious potential use for this technology is customer mapping for retail applications. Seoul Robotics asked potential buyers inside its brochure for SENSR, “want to see where your retail customers are spending the most time?” and they replied, “build a heatmap.” The company does address privacy concerns by stating that their software, “does not identify the targets, but merely tracks them, allowing this solution to be installed where cameras cannot.” Businesses could discover which areas of their store or venue are most popular and if all the spaces are being utilized to their fullest potential. E-Mart, the largest retailer in Korea, has reportedly already implemented this technology in their stores.
Another possibility is that construction companies and public works departments could use this technology to quantify stress on infrastructure by tracking vehicles on roads and bridges as well as giving city planners a better understanding of the flow of traffic in a particular area, which could lead to better information to create more secure roads with less congestion.
Although these were just a few examples, the possibilities of lidar software like SENSR that can work across numerous brands of lidar sensors are practically endless. Products like these from Seoul Robotics, ultimately, are putting lidar perception systems into more hands, which can lead to more innovation and more lidar use in general.